Summary
- By the close of 2025, Africa’s food imports are anticipated to hit $110 billion annually.
- The Maputo Declaration of 2003 urged for greater public funding in agriculture and accelerated growth in agricultural productivity.
- Crop yields in Africa are expected to rise from 1.007 billion metric tons in 2019 to 1.213 billion metric tons by 2030, with projections of 1.473 billion by 2043.
Explore More!
Agriculture plays a vital role in Africa’s economic progress, providing livelihoods for over 60% of the continent’s population. For instance, in 2023, the agricultural sector in Niger accounted for more than 47% of its GDP, while Comoros and Ethiopia contributed around 37% and 36%, respectively.
Despite its significance, Africa’s agricultural sector is faced with various hurdles, such as lack of funding, poor infrastructure, and climate change challenges. Reports indicate that Africa is set to import $110 billion worth of food each year by 2025. The presence of inexpensive commodity imports poses a significant challenge for smallholder farmers competing in the market. To combat this issue, the 2003 Maputo Declaration called for enhanced public investment in agriculture and increased productivity growth.
In response, governments, international bodies, and private investors are increasingly creating incentives to attract investment in agriculture through incentive programs. These initiatives support agribusinesses, promote sustainable farming practices, and enhance food security throughout the continent. They strive to establish a conducive environment where farmers, agribusinesses, and entrepreneurs can obtain essential resources, expertise, and market chances to flourish.
Since the introduction of these initiatives, there have been noticeable advancements. Crop production in Africa has consistently risen, with 1.007 billion metric tons produced in 2019—up from 365 million metric tons in 1990. Projections indicate further growth to 1.213 billion metric tons by 2030 and 1.473 billion metric tons by 2043.
This article showcases the Top 10 Agricultural Investment Incentive Programs in Africa for 2025, offering a detailed examination of key initiatives transforming the agricultural landscape.
Discover the Top 10 Agricultural Investment Incentive Programs in Africa for 2025!
[Note: The following list is not ranked]
1. Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP)
- Overview: CAADP, led by the African Union, focuses on enhancing agricultural productivity and investment throughout Africa.
- Key Features:
- Aims to increase agricultural productivity by a minimum of 6% annually.
- Encourages nations to allocate at least 10% of their national budgets to agriculture.
- Emphasizes improving food security and alleviating poverty.
- Impact: CAADP has played a crucial role in shaping agricultural policies and attracting investments in several African countries.
2. Green Investment Program for Africa (GIPA)
- Overview: Managed by the African Development Bank, GIPA focuses on increasing climate finance and green technologies in Africa.
- Key Features:
- Supports sustainable agriculture projects and renewable energy initiatives.
- Offers funding and technical support for eco-friendly projects.
- Impact: GIPA has enabled the advancement of numerous climate-smart agricultural initiatives across the continent.
3. Financing for Agri-SMEs in Africa (FASA)
- Overview: FASA is a fund that facilitates financing for agricultural SMEs by supporting investment vehicles within the sector.
- Key Features:
- Provides capital to small and medium-sized enterprises engaged in agriculture.
- Aims to improve access to finance for these businesses.
- Impact: FASA has been essential in enhancing the financial inclusion of agri-SMEs, thus supporting agricultural sector growth.
4. Aceli Africa
- Overview: Aceli Africa seeks to spur growth and impact within agricultural SMEs by addressing funding gaps.
- Key Features:
- Offers financial products tailored specifically for agri-SMEs.
- Focuses on increasing the capacity of financial institutions to lend to agriculture.
- Impact: Aceli Africa has increased investments in agriculture, resulting in higher productivity and sustainability.
5. SAIS Investment Readiness Programme
- Overview: This program provides a year-long tailored development plan for African tech startups in agriculture, livestock, and climate sectors.
- Key Features:
- Offers mentorship and skill-building support.
- Prepares startups for upcoming investment opportunities.
- Impact: Many startups have successfully scaled their operations and attracted investments through this program.

6. Market Access Africa 2025
- Overview: This initiative targets agro-processing, regional trade integration, and innovation to foster long-term economic growth in Africa’s agricultural realm.
- Key Features:
- Encourages regional trade and integration.
- Promotes innovation in agro-processing.
- Impact: This initiative has played a significant role in developing strong agricultural value chains across Africa.
7. BRICS+ Agriculture Investment & Trade Summit 2025
- Overview: This summit aims to unlock global opportunities in Africa, particularly for women agripreneurs.
- Key Features:
- Focuses on empowering women within the agricultural sector.
- Provides a networking and investment platform.
- Impact: The summit has led to a surge in investments in women-led agricultural ventures.
8. AgDevCo Funding Initiative
- Overview: AgDevCo specializes in investing in African agribusinesses, providing funding to scale up their operations and enhance productivity.
- Key Features:
- Offers long-term, patient capital to agribusinesses.
- Focuses on sustainable and inclusive growth.
- Impact: Investments from AgDevCo have contributed to the creation of various successful agribusinesses throughout Africa.
9. African Development Bank’s Agro-Processing Zones Initiative
- Overview: The African Development Bank is raising $2.2 billion to create agricultural processing zones in 28 Nigerian states, aiming to improve food security and generate jobs.
- Key Features:
- Sets up processing facilities close to farmers.
- Intends to minimize post-harvest losses and enhance value chains.
- Impact: The project is anticipated to strengthen food security and create job opportunities in Nigeria.
10. Helios Africa Climate Fund
- Overview: Helios Investment Partners has gathered an initial $200 million for its climate fund focused on Africa, aimed at facilitating green transitions across the continent.
- Key Features:
- Invests in low-carbon energy, climate-smart agriculture, and other environmentally sustainable fields.
- Offers financial support to climate-focused entrepreneurs.
- Impact: The fund aspires to be the largest climate fund focused on Africa, promoting sustainable development throughout the continent.
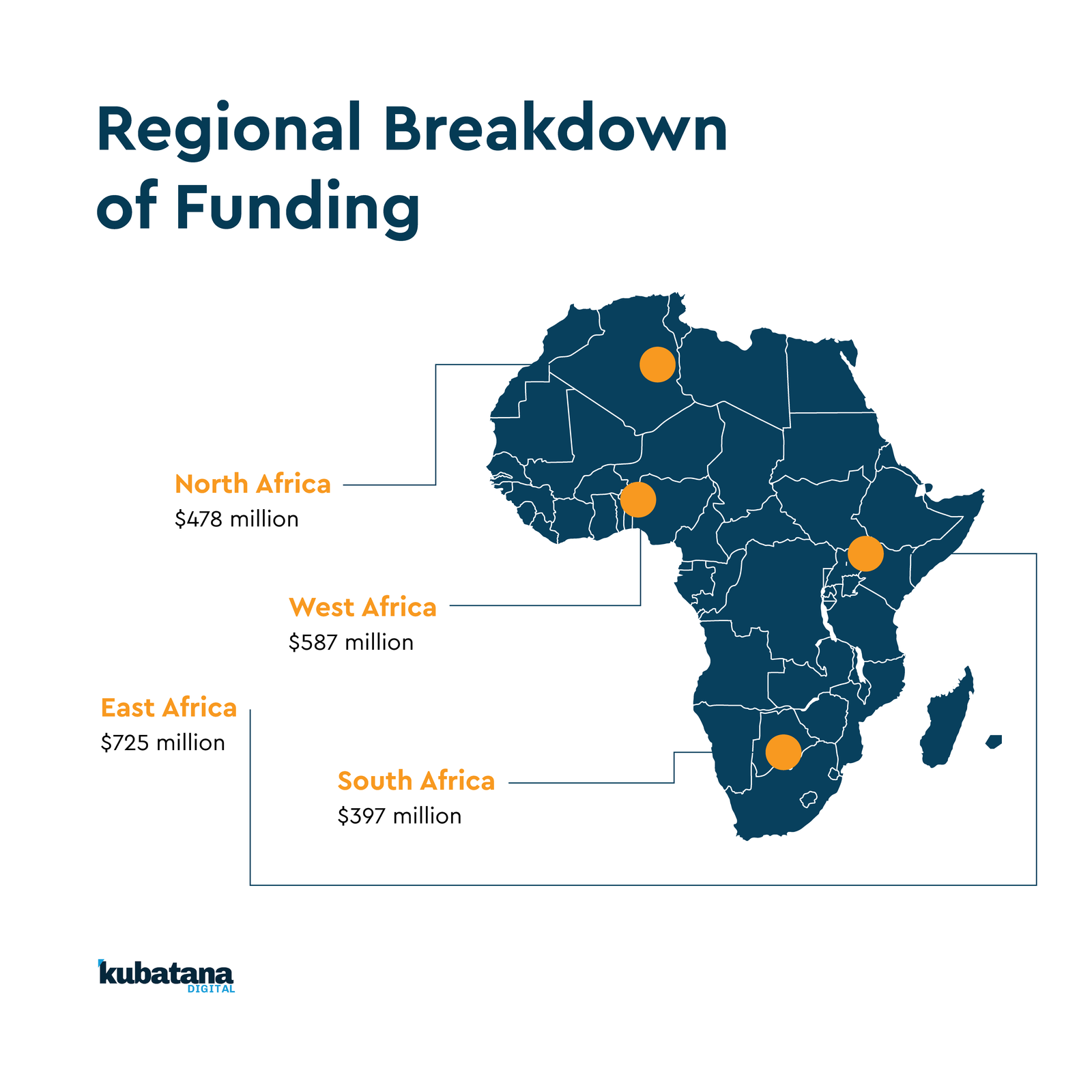
Conclusion:
These initiatives are designed not only to boost agricultural productivity and sustainability but also to tackle significant challenges like food insecurity, rural poverty, and the ecological effects of conventional farming methods. Through direct funding, skill enhancement, and fostering international trade partnerships, these programs play a vital role in ensuring long-term growth and resilience within the sector.
They embody a collective effort by governments, development organizations, and the private sector to reshape Africa’s agricultural framework. By providing financial backing, technical support, and market access, these initiatives aim to improve productivity, sustainability, and resilience in agriculture. Investors and entrepreneurs will find ample opportunities to participate in Africa’s thriving agribusiness landscape.


